G-agents derivatization for LC-MS analysis
A methodology for sensitive determination of sarin (GB), soman (GD) and cyclosarin (GF) chemical warfare agents in aqueous media was developed. The method incorporates derivatization with 2-[(dimethylamino) methyl]phenol (2-DMAMP) (a commercially available, water-soluble reagent), followed by LC-ESI-MS/MS analysis in the positive ion mode. Five derivatization agents were characterized for their MS/MS fragmentation patterns, and their reaction time, temperature and derivatization-reagent amount were optimized. The developed derivatization reaction is simple, fast (1 min) and proceeds at ambient temperature. Sample preparation consists of only the addition of the reagent directly into an injection vial prior to LC-ESI(+)-MS/MS analysis.
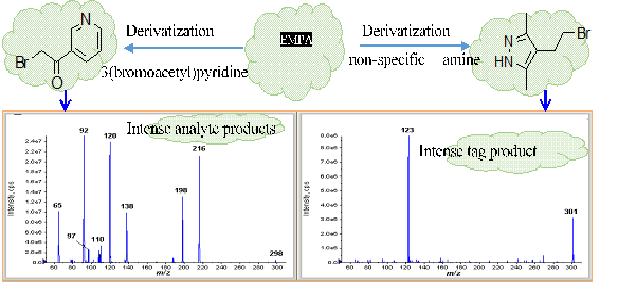
Organophosphorus acids derivatization for LC-MS analysis
One of our research interests focuses on making advances in identification by mass spectrometry, especially by using derivatizing agents to enhance the sensitivity and specificity of small molecules.
Negative electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (ESI-MS/MS) is the first choice for detecting and identifying organophosphorus acids such as alkyl methylphosphonic acids, dialkyl phosphates, and dialkyl thiophosphates. However, chemical noise in the lower mass regions of precursor and product ions, ion suppression and poor chromatographic retention of small, highly-polar acids, render the identification of such acids difficult, especially in complex matrices. To address this difficulty, we explored charge-reversal derivatizations of several polar organophosphorus acids with commercially available, mostly pyridine-based reagents,that possess high proton-affinity amines. After derivatization, the samples were analysed by LC-ESI(+)-MS/MS, the resulting acid-derivatives were better retained by LC and well responded in ESI-MS/MS in positive-ion mode.